INDICATIONS
Repatha® is indicated:
- To reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular (CV) events (CV death, myocardial infarction, stroke, unstable angina requiring ...
Repatha® is indicated:
Repatha® + statin was proven to reduce the risk of composite CV events by 20% in a median of only 2.2 years, and the benefit improved over time in the study1,2
Key secondary endpoint: composite of time to first occurrence of CV death, MI, or stroke1,2
*Not statistically significant.
FOURIER CV Outcomes Trial: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, event-driven trial of 27,564 patients with established CVD and LDL-C ≥70 mg/dL and/or non–HDL-C ≥100 mg/dL, despite high- or moderate-intensity statin therapy. Patients received either subcutaneous injections of Repatha® (evolocumab 140 mg every 2 weeks or 420 mg once monthly) or placebo. The median baseline LDL-C was 92 mg/dL.1,2
CI = confidence interval; CV = cardiovascular; HDL-C = high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HR = hazard ratio; LDL-C = low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; MI = myocardial infarction; P = P value; RRR = relative risk reduction.
ARR = absolute risk reduction; CI = confidence interval; CV = cardiovascular; HR = hazard ratio; MI = myocardial infarction.
ARR = absolute risk reduction; CI = confidence interval; CV = cardiovascular; HR = hazard ratio; MI = myocardial infarction; PCI = percutaneous coronary intervention; RRR = relative risk reduction.
ARR = absolute risk reduction; CI = confidence interval; CV = cardiovascular; HR = hazard ratio; MI = myocardial infarction; RRR = relative risk reduction.
ARR = absolute risk reduction; CI = confidence interval; CV = cardiovascular; HR = hazard ratio; MI = myocardial infarction; PAD = peripheral artery disease; RRR = relative risk reduction.
ASCVD = atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; CI = confidence interval; LDL-C = low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
*Threshold for very high-risk ASCVD patients.
†The 2022 ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway (referred herein as ACC Consensus Pathway) was designed to address current gaps in care for LDL-C lowering to reducing ASCVD risk. This effort relies extensively on the evidence established by the 2013 ACC/AHA and 2018 AHA/ACC/Multisociety cholesterol guidelines, and provides further recommendations regarding the use of newer nonstatin therapies. It should be noted that this process did not involve formal systematic reviews, grading of evidence, or synthesis of evidence. The goal was to provide practical guidance for situations not covered by the previously published guidelines until the next round of formal review of scientific evidence.13
In a descriptive, retrospective analysis of 186,670 ASCVD patients with index LDL-C >70 mg/dL (mean index LDL-C of 108 mg/dL):
who intensified statins achieved LDL-C values ≤70 mg/dL14,*
who added ezetimibe to statin therapy achieved LDL-C values ≤70 mg/dL14,*
Patients were identified between January 1, 2012 and August 31, 2014, using the IQVIA US ambulatory electronic medical record database. Treatment exposure to statin and/or ezetimibe was based on observation of a valid prescription record in the EMR database, which does not guarantee that the patient filled the prescription or used the medication. This was a descriptive, retrospective analysis that evaluated the associations between exposures and outcomes but no causal relationships can be established from this observation study.14
*Baseline statin intensity: Among the 75,523 patients with ASCVD treated at baseline, 12.18% were on low statin intensity, 58.4% were on moderate statin intensity, 20.6% were on high-statin intensity, and 8.8% were treated with other lipid-lowering agents.14
ASCVD = atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; EMR = electronic medical record; IQVIA = IMS Quintiles Virtual Information Access; LDL-C = low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Repatha® has been studied in
51
Clinical Trials15
| Repatha® + statin N=13,784 Median achieved LDL-C† 26 mg/dL1 | Statin + placebo N=13,780 Median achieved LDL-C† 89 mg/dL1 | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | n=13,769 | n=13,756 |
| Adverse events (% of patients) | ||
| Diabetes | 8.8 | 8.2 |
| Adjudicated case of new-onset diabetes | 8.1 | 7.7 |
| Nasopharyngitis | 7.8 | 7.4 |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 5.1 | 4.8 |
| Muscle-related event | 5.0 | 4.8 |
| Allergic reaction | 3.1 | 2.9 |
| Injection-site reaction | 2.1 | 1.6 |
| Cataract | 1.7 | 1.8 |
| Neurocognitive event | 1.6 | 1.5 |
| Rhabdomyolysis | 0.1 | 0.1 |
Hemorrhagic stroke: 0.21% statin + Repatha® (n=13,784), 0.18% statin + placebo (n=13,780).‡
†Median LDL-C achieved at 48 weeks.
‡The total number of patients were 8,337 in the Repatha® + statin group and 8,339 in the placebo + statin group because patients with prevalent diabetes at the start of the trial were excluded.
FOURIER-OLE is the longest trial of PCSK9i mAb to date, with some Repatha® patients followed continuously for up to 8.4 years across FOURIER and FOURIER-OLE16
No new safety signals were detected, and the incidence of serious AEs did not increase over time. The incidence of serious AEs was similar in patients achieving very low LDL-C levels (<20 mg/dL) and those with higher LDL-C12,16
Discontinuation rate due to AEs attributed to Repatha® during FOURIER-OLE was 0.1%12,§
FOURIER Open-Label Extension Study (FOURIER-OLE): Open-label extension of FOURIER trial. Analyses were pooled across the two OLE studies. 6,635 patients received Repatha® 140 mg every 2 weeks or 420 mg once a month (3,355 randomized to Repatha®, 3,280 to placebo in the parent trial). Median time on therapy was 7.1 years for those originally randomized to Repatha® (evolocumab) and 5 years for those originally randomized to placebo in the parent trial. The primary endpoint was the subject incidence of treatment-emergent events.
AEs = adverse events; CV = cardiovascular; LDL-C = low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; mAb = monoclonal antibody; OLE = open-label extension; PCSK9i = proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor.
§Consider open-label extension study limitations when interpreting the results. The open-label extension study is not blinded, not controlled, and includes inherent self-selection bias.
EBBINGHAUS studied 1,974 patients from the FOURIER CV Outcomes Trial1
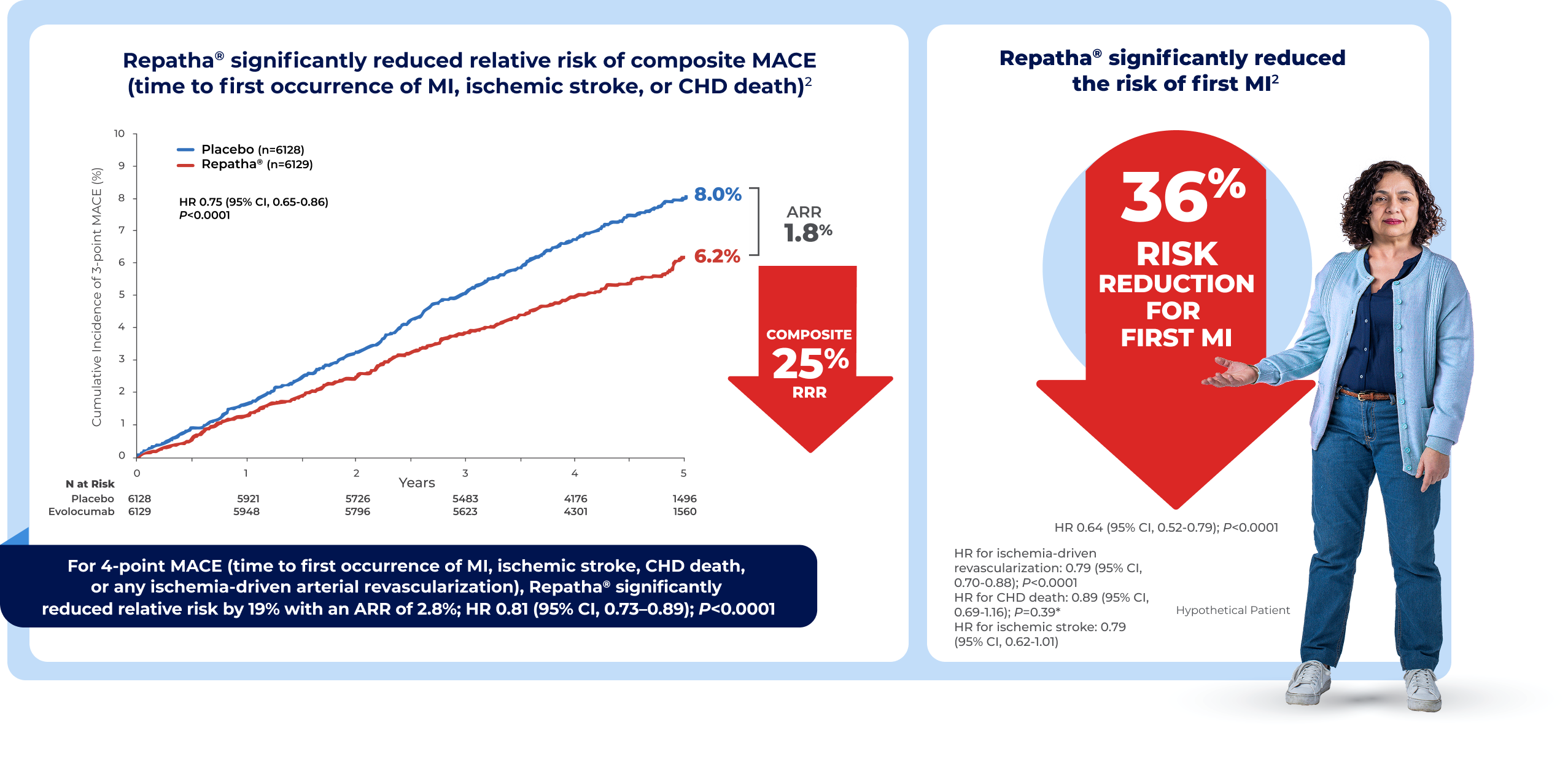

VESALIUS-CV Trial: A phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, global trial evaluating the impact of evolocumab on major cardiovascular events in patients at high CV risk without prior MI or stroke (N=12,257). Includes patients with significant CAD without MI, significant atherosclerotic cerebrovascular disease without stroke, significant PAD, and/or high-risk diabetes (defined as diabetes that is long-standing [≥10 years], complicated by microvascular disease, or daily insulin use). All patients had at least 1 additional high-risk criterion (examples include age ≥65 years; current tobacco use; and LDL-C ≥130 mg/dL, or non-HDL-C ≥160 mg/dL or ApoB ≥120 mg/dL). Patients received either subcutaneous injections of Repatha® (140 mg) or matching placebo every 2 weeks in addition to stable, optimized LLT. At baseline, median LDL-C was 122 mg/dL and median age was 66.1,2
ApoB = apolipoprotein B; ARR = absolute risk reduction; CAD = coronary artery disease; CHD = coronary heart disease; CI = confidence interval; CV = cardiovascular; HDL-C = high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HR = hazard ratio; LDL-C = low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LLT = lipid-lowering therapy; MACE = major adverse cardiac events; MI = myocardial infarction; P = P value; PAD = peripheral artery disease; RRR = relative risk reduction.
*CHD death was not statistically significant; therefore, subsequent secondary endpoints, including ischemic stroke, were not formally tested and should be interpreted as exploratory.1


*According to VESALIUS-REAL, a real-world global retrospective observational study that showed lipid management patterns in patients at high CV risk without prior MI or stroke. ~280,000 were US patients and had a history of CAD, PAD, CeVD, or high-risk diabetes. Median baseline LDL-C was 119 mg/dL. 60% of these patients were not receiving LLT at index (earliest date when patients met all eligibility criteria). Within 1 year of follow-up, 49.9% of patients had ≥1 LDL-C result (n=178,361).3
In a study using NHANES data assessing US adults with ASCVD and diabetes, lowering LDL-C provided the greatest impact on reduction in risk of recurrent ASCVD events
Based on an analysis of US adults with ASCVD and diabetes who had LDL-C ≥70 mg/dL, HbA1c ≥7% and BMI ≥27 kg/m2 (N=111, representing ~1.53 million US patients). A validated TIMI risk score calculator was used to predict the 3-year relative risk reduction of the composite of fatal or nonfatal MI or IS by lowering LDL-C to 70 mg/dL or 55 mg/dL BMI to 25 kg/m2, and HbA1c to 7%.4


LDL-C = low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
*Standard lipid-lowering treatment defined as maximally tolerated statin plus or minus ezetimibe.2
†In the overall study population, the median baseline LDL-C level was 122 mg/dL. 87% of patients were taking a statin and 72% were on high-intensity therapy. High-intensity lipid-lowering regimen was defined as daily treatment with either a high-intensity statin (eg, atorvastatin ≥40 mg daily or rosuvastatin ≥20 mg daily) or a combination of a statin at any approved daily dose and ezetimibe.1
‡The substudy was designed to measure LDL-C at the 48‑week visit.1
This subgroup analysis is exploratory and no statistical conclusion can be drawn.


Analysis conducted in the safety population, which includes all patients who underwent randomization and received at least one dose of Repatha®. Counts are shown for the number of patients with relevant events and the proportion is the number of patients with a relevant event divided by the total number of patients in the safety population.5


AEs = adverse events; ApoB = apolipoprotein B; ASCVD = atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; BMI = body mass index; CAD = coronary artery disease; CeVD = cerebrovascular disease; CHD = coronary heart disease; CV = cardiovascular; DM = diabetes mellitus; HbA1c = hemoglobin A1C; HDL-C = high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; IDR = ischemia-driven arterial revascularization; IS = ischemic stroke; LDL-C = low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LLT = lipid-lowering therapy; MACE = major adverse cardiovascular events; MI = myocardial infarction; NHANES = National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; PAD = peripheral artery disease; Q2W = every 2 weeks; SC = subcutaneous.
*IDR is defined as arterial revascularization of any vascular bed, including coronary, cerebrovascular, or peripheral arteries, performed in the presence of ischemia of the relevant end-organ.1
†High-intensity lipid-lowering regimen was defined as daily treatment with either a high-intensity statin (eg, atorvastatin ≥40 mg daily or rosuvastatin ≥20 mg daily) or a combination of a statin at any approved daily dose and ezetimibe.1
Contact MSL
Enter your ZIP code to find your local MSL. You can reach out to discuss the scientific and clinical components of this data further:
References: 1. Repatha® (evolocumab) prescribing information, Amgen. 2. Sabatine MS, Giugliano RP, Keech AC, et al; FOURIER Steering Committee and Investigators. Evolocumab and clinical outcomes in patients with cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:1713-1722. 3. Gencer B, Mach F, Murphy SA, et al. Efficacy of evolocumab on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with recent myocardial infarction: a prespecified secondary analysis from the FOURIER trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2020;5:952-957. 4. Gencer B, Mach F, Murphy SA, et al. Efficacy of evolocumab on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with recent myocardial infarction: a prespecified secondary analysis from the FOURIER trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2020;5:952-957. Supplementary Online Content. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2020.0882 5. Jernberg T, Hasvold P, Henriksson M, Hjelm H, Thuresson M, Janzon M. Cardiovascular risk in post-myocardial infarction patients: nationwide real world data demonstrate the importance of a long-term perspective. Eur Heart J. 2015;36:1163-1170. 6. Furtado RHM, Fagundes AA, Oyama K, et al. Effects of evolocumab in patients with prior percutaneous coronary intervention: an analysis from the FOURIER trial. Presented at: American Heart Association Scientific Sessions 2020; November 13-17, 2020. 7. Furtado RHM, Fagundes AA Jr, Oyama K, et al. Effect of evolocumab in patients with prior percutaneous coronary intervention. Circ Cardiovasc lnterv. 2022;15:e011382. 8. Sabatine MS, Leiter LA, Wiviott SD, et al. Cardiovascular efficacy & safety of evolocumab in diabetes, and risk of development of diabetes: an analysis from the FOURIER trial. Presented at: 53rd Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes; Lisbon, Portugal; September 15, 2017. 9. Sabatine MS, Leiter LA, Wiviott SD, et al. Cardiovascular safety and efficacy of the PCSK9 inhibitor evolocumab in patients with and without diabetes and the effect of evolocumab on glycaemia and risk of new-onset diabetes: a prespecified analysis of the FOURIER randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5(12):941-950. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30313-3 10. Bonaca MP, Nault P, Giugliano RP, et al. Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol lowering with evolocumab and outcomes in patients with peripheral artery disease: insights from the FOURIER Trial (Further Cardiovascular Outcomes Research with PCSK9 Inhibition in Subjects With Elevated Risk). Circulation. 2018;137:338-350. 11. Data on file, Amgen; 2022. 12. O’Donoghue ML, Giugliano RP, Wiviott SD, et al. Long-term evolocumab in patients with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2022;146:1109-1119. 13. Lloyd-Jones DM, Morris PB, Ballantyne CM, et al. 2022 ACC expert consensus decision pathway on the role of nonstatin therapies for LDL-cholesterol lowering in the management of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk: a report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;80:1366-1418. 14. Chen C-C, Rane PB, Hines DM, Patel J, Harrison DJ, Wade RL. Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol outcomes post-non-PCSK9i lipid-lowering therapies in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and probable heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia patients. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018;14:2425-2435. 15. Data on file, Amgen; 2025. 16. Gaba P, O’Donoghue ML, Park J-G, et al. Association between achieved low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and long-term cardiovascular and safety outcomes: an analysis of FOURIER-OLE. Circulation. 2023;147:1192-1203. 17. Giugliano RP, Mach F, Zavitz K, et al. Cognitive function in a randomized trial of evolocumab. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:633-643.
References: 1. Bohula EA, Marston NA, Bhatia AK, et al. Evolocumab in patients without a previous myocardial infarction or stroke. N Engl J Med. Published online November 8, 2025. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2514428 2. Bohula EA, Marston NA, Ruzza A, et al. Rationale and design of the effect of evolocumab in patients at high cardiovascular risk without prior myocardial infarction or stroke (VESALIUS-CV) trial. Am Heart J. 2024:269:179-190. 3. Chan Q, Sakhuja S, Ochs A, et al. Lipid-lowering therapy use in high-risk ASCVD patients without prior MI or stroke—preliminary data from VESALIUS-REAL, US. Poster presented at: American College of Cardiology Annual Meeting; March 29–31, 2025; Chicago, IL, USA. 4. Wong ND, Karthikeyan H, Fan W, Dhalwani N, Head L, Jin R. Assessment of risk reduction of recurrent cardiovascular events in patients with ASCVD and diabetes. Oral presentation presented at: ObesityWeek 2025; November 4–7, 2025; Atlanta, GA. 5. Bohula EA, Marston NA, Bhatia AK, et al. Evolocumab in patients without a previous myocardial infarction or stroke. N Engl J Med. Supplement. Published online November 8, 2025. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2514428