INDICATIONS
Repatha® is indicated:
- To reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular (CV) events (CV death, myocardial infarction, stroke, unstable angina requiring ...
Repatha® is indicated:
Every
A patient has an MI3
A patient has a stroke3
did not have a lipid test in the year following their most recent MI4,†
treated with low-to-moderate-intensity statin ± ezetimibe did not achieve LDL-C <55 mg/dL4,†
treated with high-intensity statin ± ezetimibe did not achieve LDL-C <55 mg/dL4,†
– Dr. Turnbo



High-Risk Factors
Hypothetical Patient
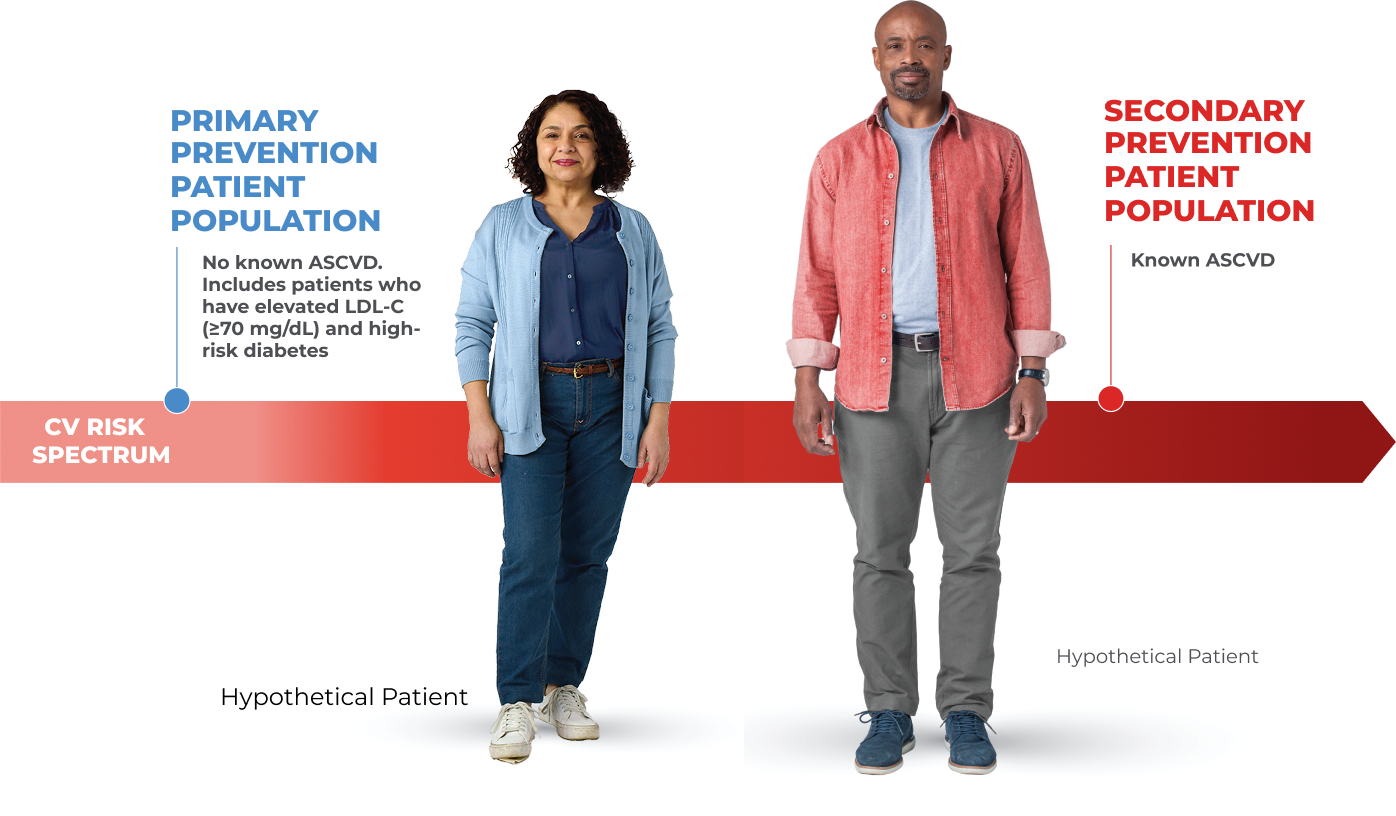
Help patients at high CV risk without prior MI or stroke reduce their risk of MACE (CV death, myocardial infarction, stroke, unstable angina requiring hospitalization, or coronary revascularization).
Hypothetical Patient
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) considers patients at high risk of ASCVD based on the following:
ASCVD risk factors include:



Very High-Risk Factors
Hypothetical Patient
Help patients with a prior CV event reduce their risk of MACE (CV death, myocardial infarction, stroke, unstable angina requiring hospitalization, or coronary revascularization).
Hypothetical Patient
2018 AHA/ACC/MULTISOCIETY GUIDELINE DEFINITION OF A VERY HIGH-RISK ASCVD PATIENT10
94% of patients with a history of major ASCVD events had additional risk factors that placed them in the very high-risk category11,‡
Continuing the commitment to help
patients reach their recommended LDL-C

Duration: 5:14 minutes
*The data were taken from The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation’s Global Burden of Disease Study. The open source data were used to determine the incidence of new clinical ASCVD cases, defined as: ischemic heart disease, stroke, ischemic stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
†Retrospective patient study from IQVIA using an anonymized patient claims data set encompassing nearly 5.4 million patients who experienced Ml and met criteria for VHR ASCVD. Data set from January 1, 2018, to December 31, 2022. 17.1% of patients were treated with low-to-moderate-intensity statin ± ezetimibe, 40.4% high-intensity statin ± ezetimibe, and 44.2% untreated with lipid-lowering therapy. LDL-C levels for this analysis were available for 441,736 VHR ASCVD patients following their most recent MI.
‡A retrospective cohort study of 16,344 patients 19 years of age or older with a history of major ASCVD events using data from the MarketScan database. 5,919 patients had symptomatic PAD as their history of a major ASCVD event. Patients were followed from January 1, 2016 through December 31, 2017 for recurrent ASCVD events. Major ASCVD events included recent ACS, history other than a recent ACS, history of ischemic stroke, and symptomatic PAD.
ACS = acute coronary syndrome; ADA = American Diabetes Association; ASCVD = atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; BMI = body mass index; CAC = coronary artery calcium; CKD = chronic kidney disease; CV = cardiovascular; CVD = cardiovascular disease; IQVIA = IMS Quintiles Virtual Information Access; LDL-C = low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; MACE = major adverse cardiac events; MI = myocardial infarction; PAD = peripheral artery disease; VHR = very high risk.